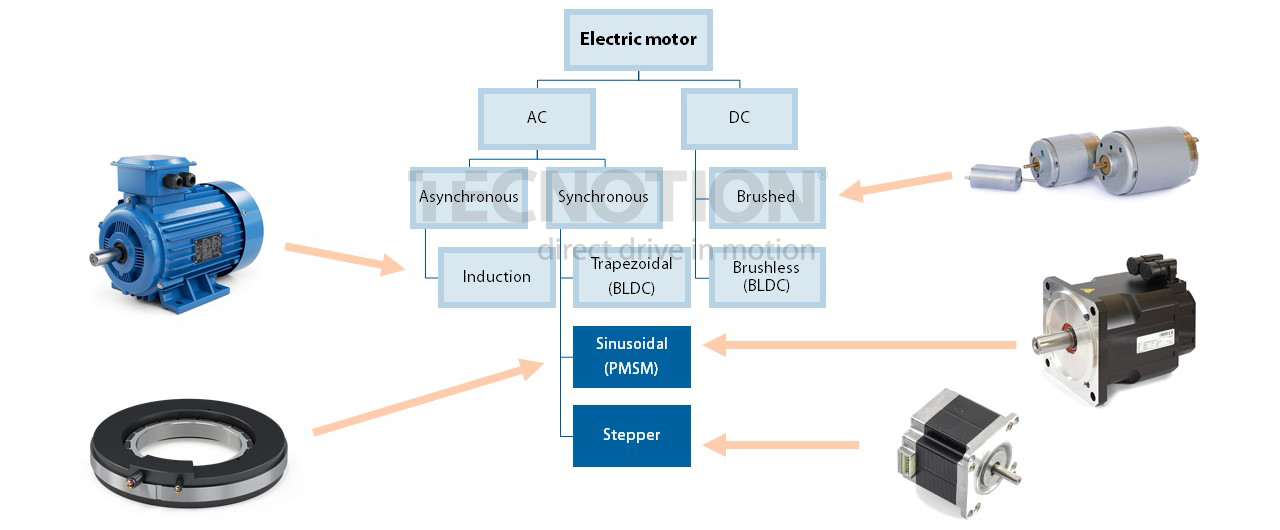
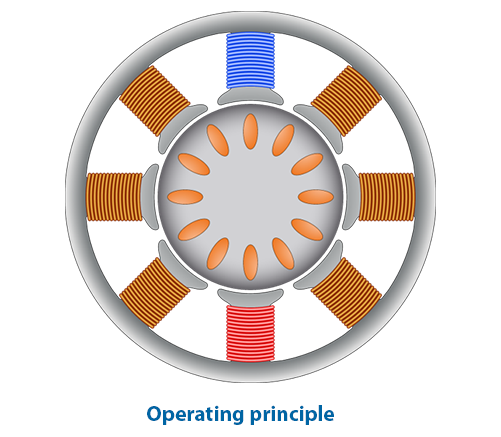
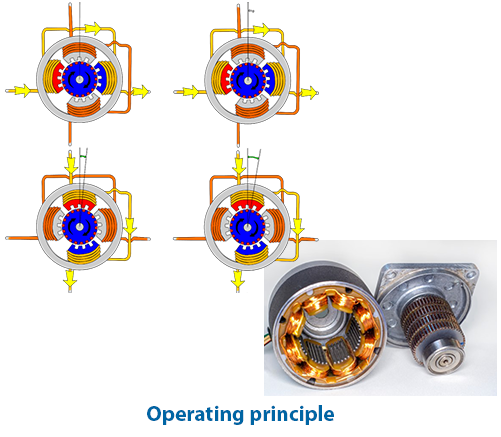
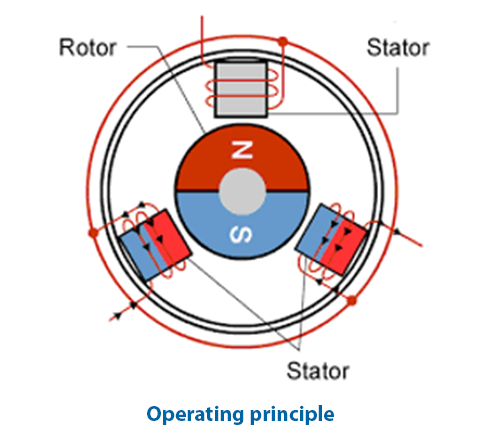
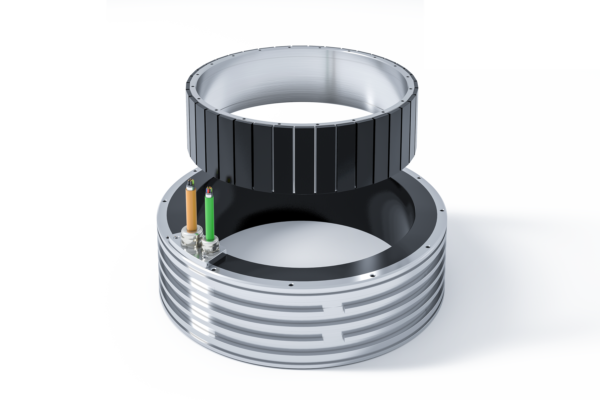
Torque motors vs Conventional servo motors
Different motor types are used to provide rotary motion within industrial applications. Each application has different requirements for speed, torque and accuracy, as well as its constraints in build-in volume and budget. This page briefly introduces different types of motors and their performance in positioning/indexing applications. Please watch our webinar recording to find out more in-depth information.