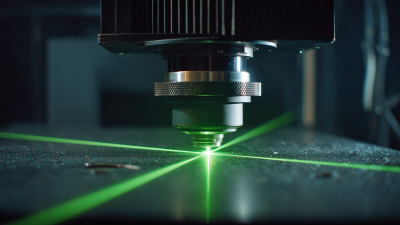
Unlocking the Power of Laser CNC Machines for Metal Precision Cutting and Fabrication Techniques
The advancement of technology in the manufacturing sector has led to a significant shift towards precision in metal cutting and fabrication techniques, particularly through the utilization of laser CNC machines. According to a recent report by Grand View Research, the global CNC laser market is projected to reach USD 2.57 billion by 2025, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.6%. This growth is largely attributed to the increasing demand for automation and precision engineering in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and construction. The integration of laser CNC machines for metal not only enhances accuracy but also reduces waste and operational costs, enabling manufacturers to meet the stringent quality requirements in today's fast-paced market. As businesses seek to improve their production processes, the role of laser CNC technology becomes increasingly pivotal, unlocking opportunities for innovation and efficiency.

The Fundamentals of Laser CNC Machines in Metalworking
Laser CNC machines have revolutionized the metalworking industry by offering unparalleled precision and versatility in cutting and fabrication techniques. At the core of their operation lies the sophisticated technology that harnesses concentrated laser beams to cut through various metals, including steel, aluminum, and titanium. Unlike traditional cutting methods, which can introduce mechanical stress and thermal distortion, laser cutting ensures a clean, precise edge with minimal heat affected zones. This capability not only enhances the quality of the workpiece but also reduces the need for extensive finishing processes.
Understanding the fundamentals of laser CNC machines is crucial for any metalworking professional. These machines utilize computer numerical control (CNC) technology to automate the cutting process, allowing for intricate designs and repeatable accuracy. Operators can input designs directly from CAD software, enabling quick adjustments and iterations. Additionally, the ability to control the depth and intensity of the laser further enhances fabrication options, making it possible to produce complex geometries that are otherwise difficult to achieve. As industries continue to seek efficiency and precision, mastering the fundamentals of laser CNC technology will be essential for staying competitive in the metalworking field.
Applications of Laser CNC Technology in Precision Cutting
Laser CNC technology has revolutionized precision cutting across various industries by providing unparalleled accuracy and efficiency. This advanced method utilizes a high-powered laser beam to cut through materials such as metal, plastic, and wood with remarkable precision. The ability to easily engrave and shape materials using laser technology has made it a preferred choice in manufacturing environments where exact dimensional tolerances are crucial. As industries increasingly embrace digital manufacturing, the integration of laser CNC systems significantly enhances productivity and reduces material wastage.
Applications of laser cutting extend beyond traditional metal fabrication; they have also penetrated specialized sectors like medical device manufacturing and oilfield equipment. In the medical field, laser technology is employed to create intricate components with minimal thermal impact, ensuring that the integrity of sensitive materials is maintained. Similarly, in oilfield operations, lasers are utilized for cutting and welding, proving indispensable for maintaining high precision in harsh environments. This versatility underscores the vital role of laser CNC technology in driving forward manufacturing innovations and meets the stringent quality demands of modern industries.
Comparative Analysis: Laser CNC vs. Traditional Metal Fabrication
Laser CNC machines have revolutionized the landscape of metal precision cutting and fabrication techniques, offering distinct advantages over traditional methods. One of the key differences lies in the precision and speed that laser cutting technology provides. Unlike conventional fabrication techniques, which often rely on mechanical cutting tools that can wear out or become inaccurate over time, laser CNC machines utilize focused light beams to achieve micrometer-level accuracy. This not only reduces material waste but also allows for intricate designs that would be difficult to replicate using traditional machinery.
Moreover, the flexibility of laser CNC machines in handling different materials is noteworthy. They can efficiently cut through various metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and brass, with minimal setup changes. In contrast, traditional methods often require specialized tools and extensive recalibration for different materials. This versatility can lead to significant time savings in manufacturing processes. Additionally, laser cutting produces cleaner edges and reduces the need for post-processing, further enhancing production efficiency when compared to traditional metal fabrication techniques.
Unlocking the Power of Laser CNC Machines for Metal Precision Cutting and Fabrication Techniques - Comparative Analysis: Laser CNC vs. Traditional Metal Fabrication
| Feature |
Laser CNC Machines |
Traditional Metal Fabrication |
| Cutting Precision |
±0.01 mm |
±0.2 mm |
| Material Versatility |
Metals, Plastics, Wood |
Primarily Metals |
| Thickness Capability |
Up to 25 mm |
Up to 50 mm |
| Cutting Speed |
High (specific speed varies) |
Moderate |
| Setup Time |
Minimal |
Higher |
| Waste Material |
Low |
Higher |
| Operating Costs |
Moderate |
Lower |
Innovations in Laser Cutting Techniques for Enhanced Efficiency
The landscape of laser cutting techniques is undergoing significant transformation, driven by advancements that enhance efficiency and precision in manufacturing processes. As the demand for high-performance laser technologies escalates, the global laser processing market is projected to reach $11.89 billion by 2032, marking a substantial increase from $7.17 billion in 2025. This growth is fueled by rapid industrial automation and the implementation of innovative laser systems that streamline production and improve cutting quality.
Moreover, recent innovations have introduced sophisticated laser CNC machines that excel in metal precision cutting. These developments not only allow for intricate designs and high tolerance levels in fabrication but also contribute to cost-saving measures through reduced waste and increased speed. By integrating advanced features such as automated adjustments and real-time monitoring, manufacturers are achieving enhanced operational efficiency, positioning themselves at the forefront of the competitive landscape in metal processing. The commitment to exploring new possibilities in laser cutting is essential for firms looking to leverage technology for superior fabricating capabilities.
Future Trends in Laser CNC Technology for the Metal Industry
The advancements in laser CNC technology are poised to revolutionize precision cutting and fabrication techniques within the metal industry. As industries evolve, the integration of high-power lasers has showcased significant improvements in cutting speed, accuracy, and versatility. These innovations enable manufacturers to tackle complex designs with ease, ultimately leading to reduced waste and enhanced productivity. With ongoing research into the applications of laser technology, such as welding and drilling, the potential for efficient and high-quality manufacturing processes continues to expand.
Future trends indicate a strong market shift towards more compact, portable laser cutting solutions, which cater to both small-scale operations and large enterprises. The rising interest in machine designs that incorporate artificial intelligence and modularity is also evident, providing opportunities for tailored solutions that adapt to specific production needs. Furthermore, as industries, particularly automotive and construction, increasingly adopt laser technology, the potential for enhanced collaboration across sectors is significant. This interconnectedness not only fosters innovation but also sets a path for sustainable production practices in the years to come.